Help
TogoVar in general
About the terms of use
About the data collected in TogoVar
- Can I retrieve phenotype information on an individual level?
- Are the data linked with information about gene expression and proteins?
- What software is used for detecting variants and how you manage the quality?
- What are the targeted variant types for TogoVar?
- How do you calculate the Consequence value?
- How do you calculate the value of Clinical significance?
- What are AlphaMissense, SIFT and PolyPhen?
- Was a liftover tool used for generating variant data?
About the TogoVar search system
- What does the frequency indicator in the Frequency column of the search results represent?
- For each variant type, how is the position, reference and alternative allele described respectively?
- In TogoVar, how is the variant described?
- Can I search by HGVS description (e.g. ALDH2:p.Glu504Lys)?
- What can I do with the Advanced search?
- Can I search for variants with different alternative allele frequencies between Japanese and other populations?
- Can I search for variants by both positions on GRCh38 and GRCh37?
TogoVar in general
What are the objectives and utilities of TogoVar?
NGS technologies have enabled large-scale genome sequencing to capture variants at low frequencies. However, existing databases do not contain sufficient variant frequency data for Japanese populations. To address this problem, TogoVar seeks to provide a reliable frequency information by assembling variant information from the NBDC Human Database/Japanese Genotype-phenotype Archive (JGA) and public Japanese genomic variation data.
In addition, since the reference human genome sequence can be updated, the genomic position may vary for the same variant if it refers to a different genome build. Thus, in our database, a unique ID is assigned to the same variant, thereby preventing the need to convert the positional information of the variant among different reference sequences, as done by researchers.
About the terms of use
Can I use the TogoVar for free?
You can use the TogoVar service for free. For the use of the database, refer to the Terms.
How to cite the TogoVar database in my publication?
Refer to the attribution (credit) display examples in Terms.
Can I use it for commercial purposes?
You are free to browse the TogoVar websites and use the docker images to be released for commercial purposes. For data created by third parties and imported in TogoVar, please follow the terms of use of each organization. For more details, refer to Terms.
About the data collected in TogoVar
Can I retrieve phenotype information on an individual level?
TogoVar database does not keep private information, and we do not currently provide phenotype information for each individual. For more details about phenotype information, please directly contact the research groups described in the JGA-WES dataset , and JGA-SNP dataset.
Are the data linked with information about gene expression and proteins?
Not yet but planned.
What software is used for detecting variants and how you manage the quality?
Refer to How JGA dataset was generated.
What are the targeted variant types for TogoVar?
There are five targeted variant types for TogoVar: SNV, Insertion, Deletion, Indel, and Substitution. Of 5 types that HGVS enumerated as the types of variants, Duplication is classified as Insertion, and Indels, for which the lengths of Insertion and Deletion are the same, are classified as Substitution. To identify the type of the variant, Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) is used.
How do you calculate the Consequence value?
The value of variant consequence in Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) is displayed. If there are multiple transcripts for a single variant, only the most critical consequence may be displayed.
How do you calculate the value of Clinical significance?
The value of clinical significance in ClinVar and clinical significance in MGeND are displayed.
What are AlphaMissense, SIFT and Polyphen?
AlphaMissense, SIFT and PolyPhen predict the impact of variants on protein function when an amino acid sequence is altered. These programs were performed using Variant Effect Predictor (VEP). The icons below represent the threshold scores used for qualitative predictions.
- AlphaMissense> 0.564Likely pathogenic≥ 0.340AmbiguousThe score thresholds for "Likely pathogenic" and "Likely benign" were chosen to classify pathogenic and benign ClinVar variants with 90% precision, respectively. See AlphaMissense in VEP Plugins for details.< 0.340Likely benign
- SIFT< 0.05DeleteriousThe score represents the normalized probability of an amino acid change being tolerated. Scores closer to zero indicate a higher likelihood of the change being deleterious. The qualitative prediction is based on this score. Substitutions with a score less than 0.05 are classified as "Deleterious", while all others are considered "Tolerated". See SIFT in Pathogenicity prediction of Ensembl Variation for details.≥ 0.05Tolerated
- PolyPhen> 0.908Probably Damaging> 0.446Possibly Damaging≤ 0.446BenignVariants are predicted as "Probably Damaging" if they have posterior probability scores indicating an estimated false positive rate (FPR) of 5% or below. Those with FPRs at or below 10% are "Possibly Damaging", while variants with FPRs above 10% are classified as "Benign". See Polyphen in Pathogenicity prediction of Ensembl Variation for details.UnknownUnknown
Was a liftover tool used for generating variant data?
Yes. Some of the GRCh38 datasets have been created by lifting over their GRCh37 datasets. Please refer to the Liftover GRCh37 column in the TogoVar datasets (GRCh38) pagefor the target datasets. A liftover tool transannohas been used since the release on November 16, 2023. CrossMapwas used until the release on July 14, 2023.
About the TogoVar search system
What does the frequency indicator in the Frequency column of the search results represent?
The frequency indicator represents the alternative allele frequency for each dataset. The color of the frequency meter corresponds to the color allocated to the dataset. The data availability or frequency value is represented on a 9-point scale.
For each variant type, how is the position, reference and alternative allele described respectively?
An example for each variant type is shown below. Note that the position of the first base in the chromosome is 1.
Variant Type | ID | Position | Ref / Alt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SNV | tgv167913215 | 12 111767141 | CA | The 111767141st base C in chromosome 12 was replaced by A. |
Ins | tgv134135934 | 12 111786238 | G | A base G was inserted between the 111786238th and 111786239th bases in chromosome 12. |
Del | tgv110307325 | 12 111778836 | A | The 111778836th base A in Chromosome 1 was deleted. |
In TogoVar, how is the variant described?
A. In TogoVar a variant is identified as a set of its genomic position, reference and alternative allele and human genome build. Examples of variant notations in TogoVar, dbSNP, VCF and HGVS are shown below.
TogoVar | dbSNP | VCF | HGVS | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ID | Position (GRCh38) | Ref / Alt | ID | Position (GRCh38) | Alleles | Position | Ref | Alt | ||||||
SNV | tgv167913215 | 12 111767141 | CA | rs567143183 | chr12:111767141 | C>A | 12:111767141 | C | A | 12:g.111767141:C>A | ||||
| tgv47263142 | CG | C>G | C | G | 12:g.111767141:C>G | |||||||||
Ins | tgv134135934 | 12 111786238 | G | rs534925026 | chr12:111786238 | insG | 12:111786238 | T | TG | 12:g.111786238_111786239insG | ||||
Del | tgv110307325 | 12 111778836 | A | rs766411401 | chr12:111778836-111778847 | delA | 12:111778835 | GA | G | 12:g.111778847del | ||||
Q: Can I search byHGVS description(e.g. ALDH2:p.Glu504Lys)?
Yes. HGVSc (e.g.ALDH2:c.1510G>A) and HGVSp (e.g.ALDH2:p.Glu504Lys) are acceptable. Variant Recoderis used to convert an HGVS description to a GRCh38/GRCh37 position.
Q: What can I do with the Advanced search?
You can build a query with an alternative allele frequency, clinical significance, and other search criteria combined with the AND and/or OR operator. See"Q: Can I search for variants with different alternative allele frequencies between Japanese and other populations?" for usage.
Can I search for variants with different alternative allele frequencies between Japanese and other populations?
Yes. You can search by Advanced search
Variant sets for comparison of alternative allele frequencies are as follows:- For Japanese populations, variants included in either GEM-J WGA or 8.3KJPN
- For gnomAD populations, variants included in either gnomAD genomes or gnomAD exomes
- Select the Advanced search tab at the top of the home page.
- Select the Alternative allele frequency/count at the Add condition menu.
- Specify a dataset (GEM-J WGA) and an alternative allele frequency (>= 0.3). You can also specify the number of alternative alleles.
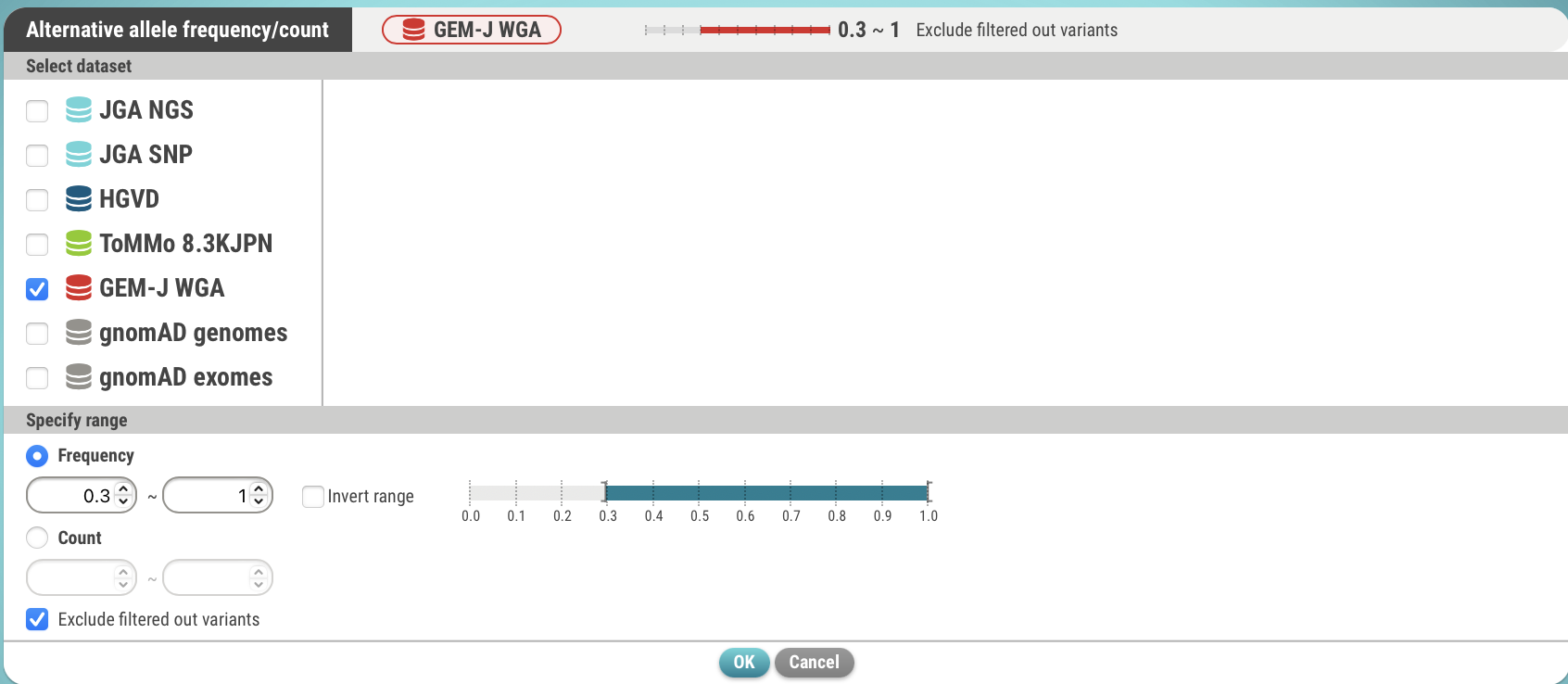
- Click the OK button. The search criteria has been set.
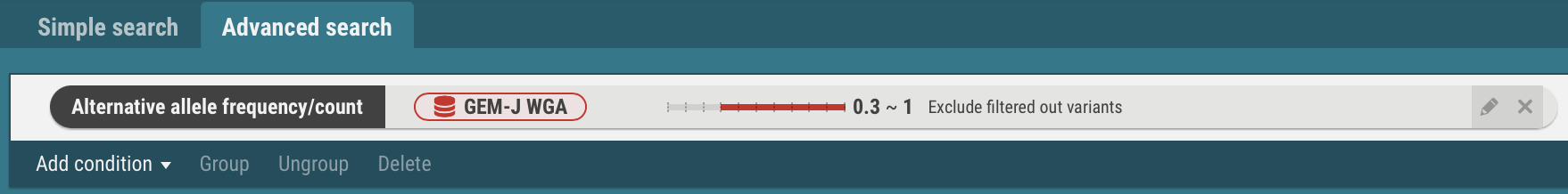
- In the same procedures, enter search criteria for the datasets, ToMMo 8.3KJPN, gnomAD genomes and gnomAD exomes.
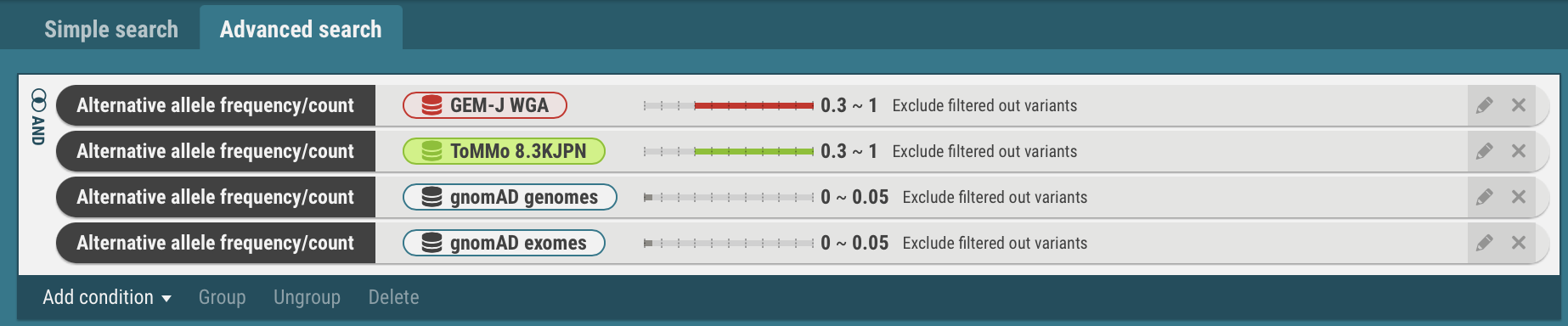
- Join the search criteria for Japanese populations, GEM-J WGA and ToMMo 8.3KJPN, with the OR operator.
- Select the search criteria for GEM-J WGA and ToMMo 8.3KJPN. The selected criteria is enclosed by yellow borders.
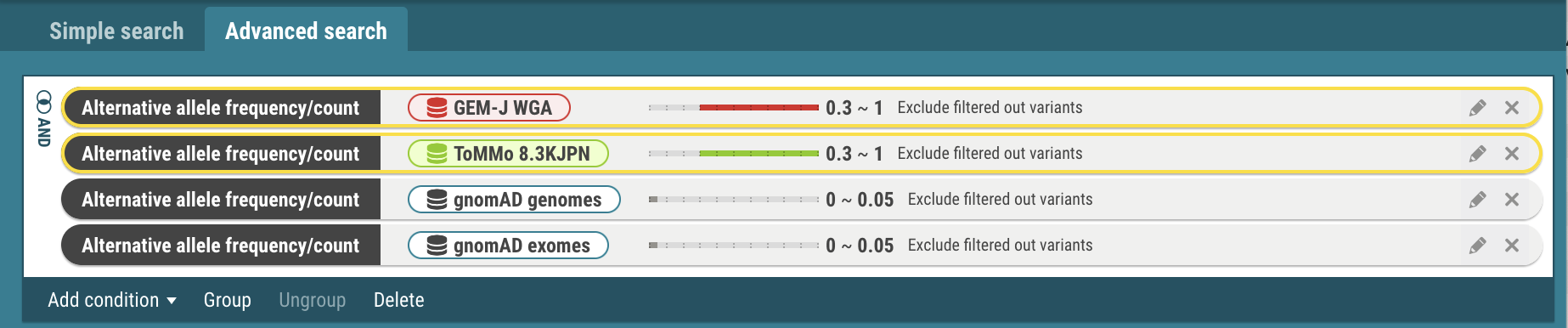
- Select the Group menu. The selected criteria are joined with the OR operator. To change to the AND operator, click the OR icon.
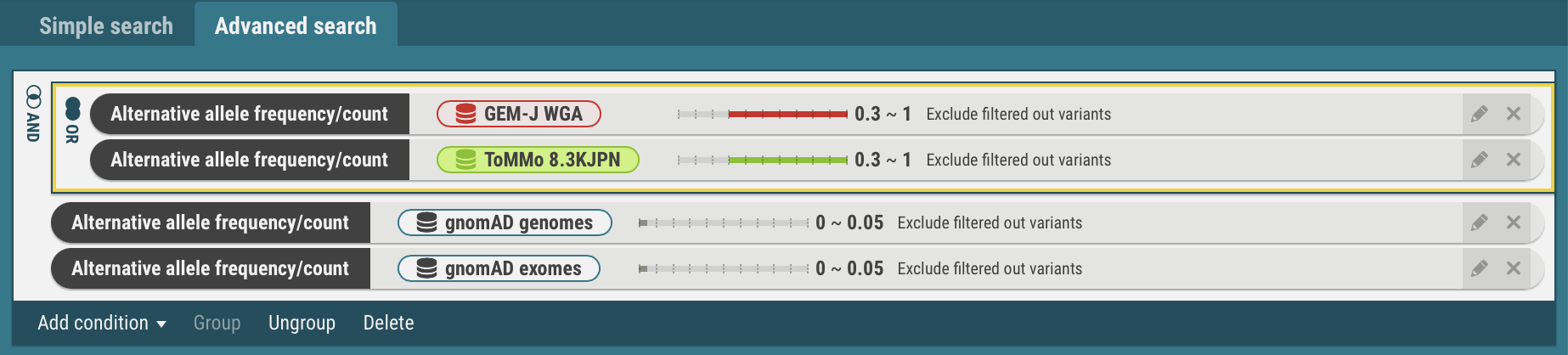
- Select the search criteria for GEM-J WGA and ToMMo 8.3KJPN. The selected criteria is enclosed by yellow borders.
- In the same procedures, the search criteria for the gnomAD genomes and gnomAD exomes are joined with the OR operator.
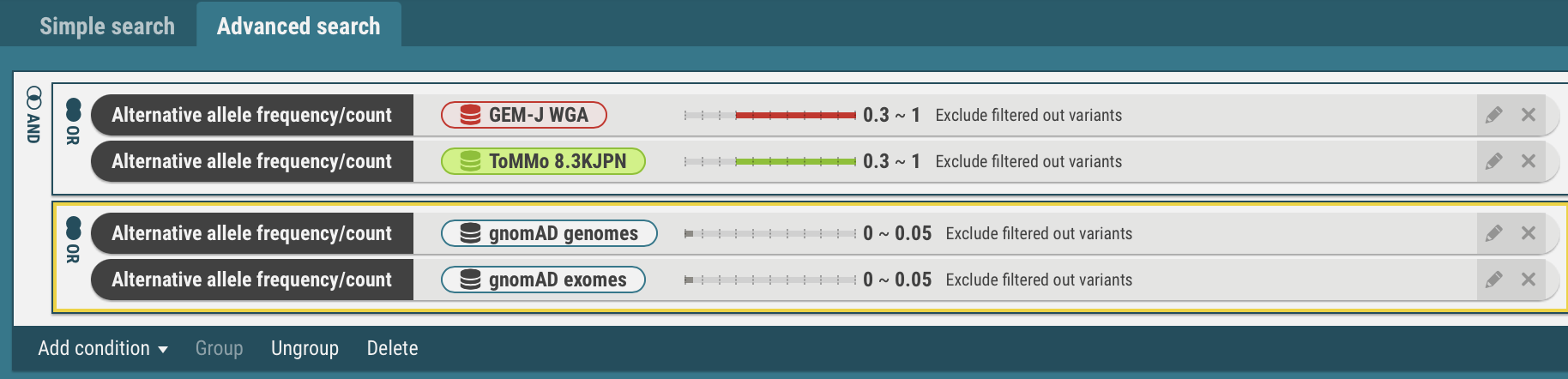
AND
(freq(gnomAD genomes) <= 0.05) OR (freq(gnomAD exomes) <= 0.05))Each time search criteria is changed, the search is automatically executed and a list of variants that match the criteria is refreshed.
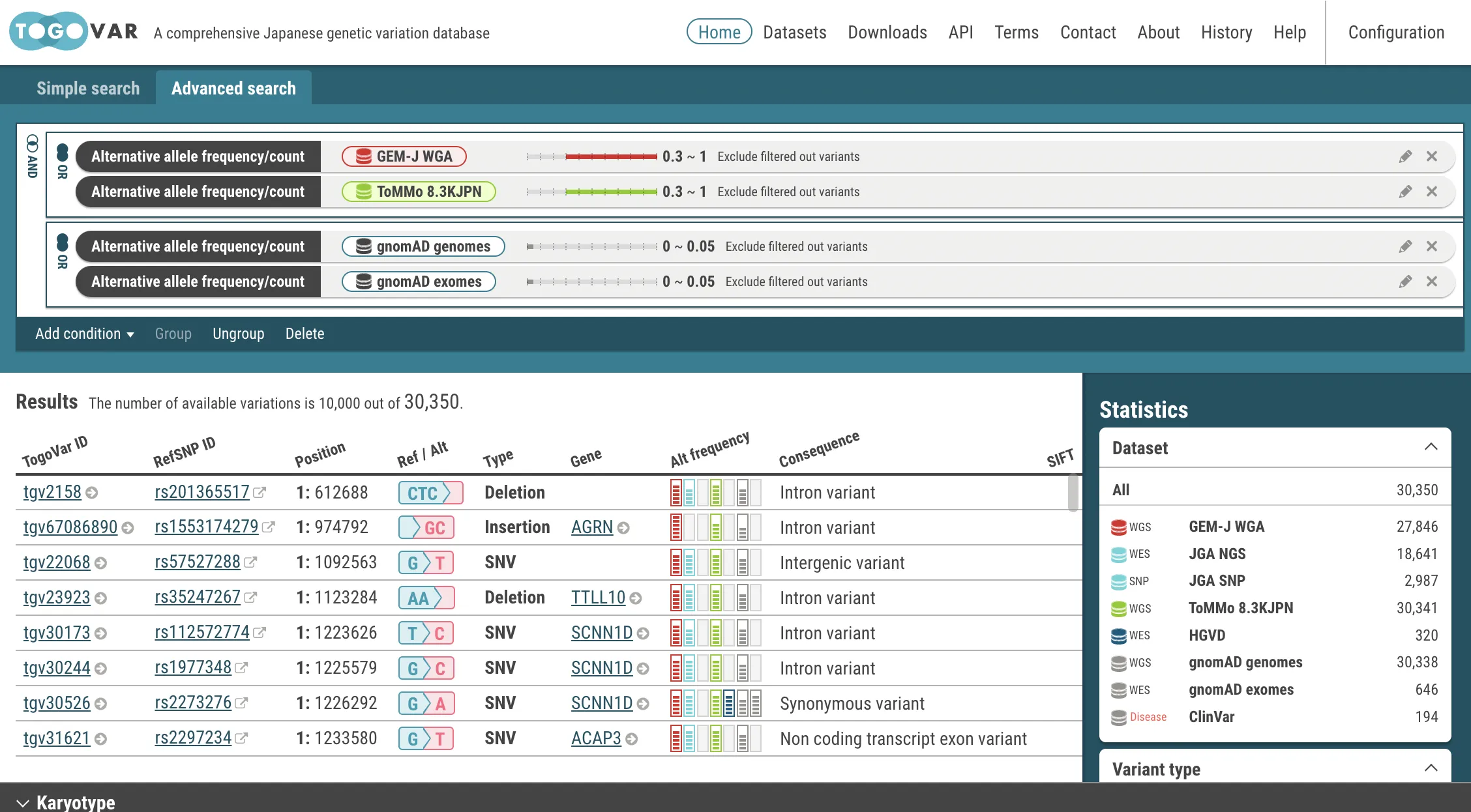 Functions in the menu bar
Functions in the menu bar- Add condition: Add search criteria to the query builder.
- Group: Combine selected search criteria indicated by yellow borders with the OR operators. Note: click the OR icon to change to the AND operator.
- Ungroup: Separate joined search criteria. This is a reverse operation of the Group menu.
- Delete: Delete selected search criteria indicated by yellow borders.
 :Edit search criteria
:Edit search criteria :Delete search criteria
:Delete search criteria
Can I search for variants by both positions on GRCh38 and GRCh37?